The protected land areas increased from 6.5% after Angola’s independence to 12.58% of the national surface area in 2013. The creation of a network of marine protected areas is expected in the near future . The Ministry of the Environment, in collaboration with the Ministry of Fisheries and the Sea, foresees the creation of a network of marine protected areas, in which a Networking Plan for Marine Protected Areas will be prepared, where the classification and characteristics of the network of marine protected areas, as well as the management and conservation measures to be applied to each of the defined protection and management classes will be proposed.
Angola’s biodiversity is very poorly known, with comparatively limited research before independence in 1975 halting altogether in the three decades of civil war and unrest that followed. In their recent book on Angola, Huntley et al. (2019) note that “most National Parks still lack the most basic management capacity and effectiveness, despite the wealth of legislation promulgated since the Base Law for the Environment was approved in 1998” and also that “Fortunately, despite the reverses of the past decades, each protected area still includes areas of sufficient dimension that can, with effective management, achieve significant biodiversity conservation goals. Since 2017, the new government leadership gives promise for a revitalised and energetic approach to conservation in Angola, as demonstrated in the recent Strategic Plan for the Conservation Areas System of Angola.”
There is an initiative to implement marine spatial planning (MSP) in Angola, and a pilot area for an experimental MSP project covering an area of approximately 107,000 km2 has recently been identified. A key element of the process is to identify and describe a network of Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (Huntley et al., 2019).
Transboundary protected and conserved areas
Angola includes part of four transboundary conservation areas, namely Iona Skeleton Coast TFCA, Kavango-Zambezi TFCA, Liuwa Plain-Mussuma TFCA, and Mayombe Forest Transfrontier Protected Area.
Policy context
A comprehensive report on legislation and policy related to protected area management, governance, and equity was undertaken by the BIOPAMA programme. It identified 35 relevant laws and policies in Angola (Tessema, 2019).
Key species
Angola is home to an incredible diversity of habitats, and therefore also to a huge variety of species. Angola has 291 native species, most of which are from the orders Rodentia (85), Chiroptera (73), Carnivora (39), and Cetartiodactyla (33). There is a large number of endemic and near endemic species, most of which are rodents or bats.
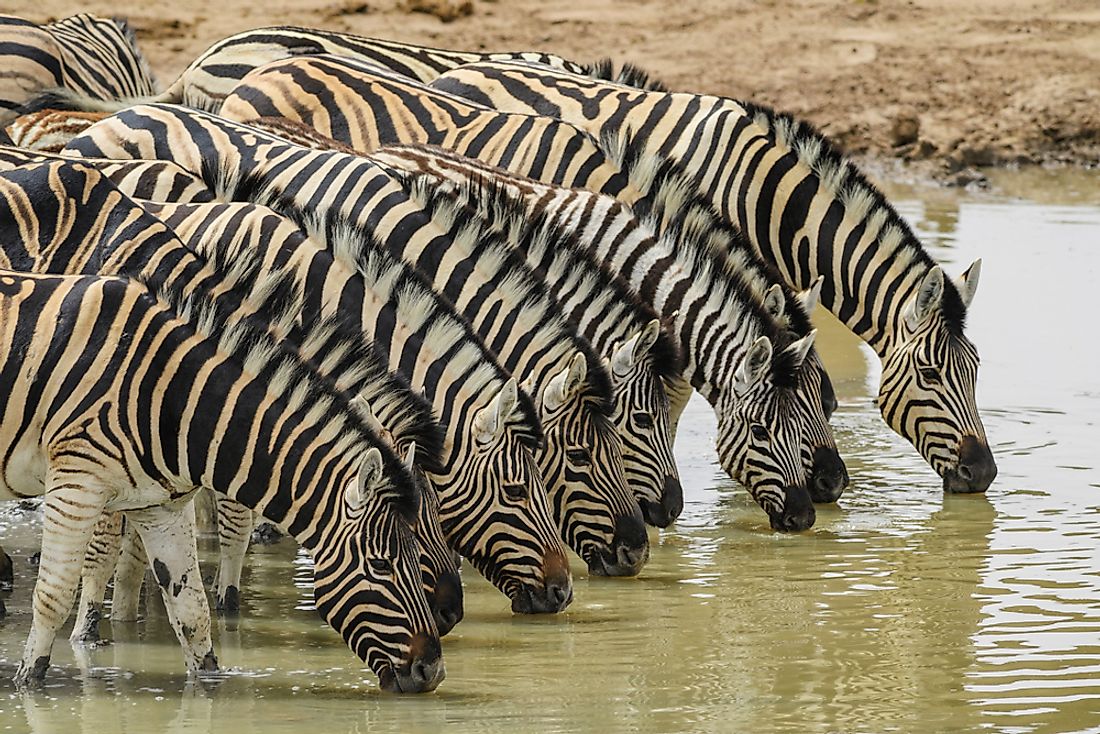
According to Angola’s Fifth National Report to the CBD, mammals of particular interest include the endemic giant sable (Hippotragus niger variani), the Western lowland gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla), the African manatee (Trichechus senegalensis), and the mountain zebra (Equus zebra). The conservation status of many of these species is poorly understood. Populations of African elephant (Loxodonta africana), hippopotamus (Hippopotamus amphibius) and brown fur seal (Arctocephalus pusillus) are considered stable.
Angola is home to 25 endemic bird species. Little is known about Angola’s diversity of microfauna and flora, but it is known that many species suffer from high harvesting levels for timber, charcoal, food, as well as local and international live trade.
Angola also has high marine and freshwater biodiversity, including five species of sea turtles, and many species of cetaceans. Small scale fishing of fish and crustaceans is a critical part of the subsistence of rural coastal communities. Mackerel has been critically overharvested, resulting in the imposition of an annual four-month ban. The introduction of alien species of tilapia is likely due to the prevalence of fish farming projects.
Pressures and threats
Angola’s biodiversity is subject to many threats and pressures. The main pressures are from habitat due to subsistence agriculture, mining, infrastructure, deforestation for charcoal and timber, and a very high incidence of fires. Poaching, including for the bushmeat trade, is also a major threat. Overfishing, particularly of mackerel, has resulted in an annual four-month ban. Angola is in the process of updating its legislation, but implementation and enforcement are required.

 Protected Areas
Protected Areas





