Eritrea has four protected areas covering 5,936 km2 of land and does not have any marine protected areas (UNEP-WCMC & IUCN (2019f). Although there are no officially gazetted protected areas in the country, there are some areas set aside for protection through government directives. The de facto protected areas have no management or business plans. A draft Protected Area Proclamation was prepared and proposed protected areas were identified in 2018.
The implementation of the proposed protected area system is hindered due to inadequate human capacity.
Transboundary protected and conserved areas
Eritrea does not have any transboundary conservation areas.
Policy context
Policy context A comprehensive report on legislation and policy related to protected area management, governance, and equity was undertaken by the BIOPAMA programme. It identified seven relevant laws and policies in Eritrea (Tessema (2019).
Key species
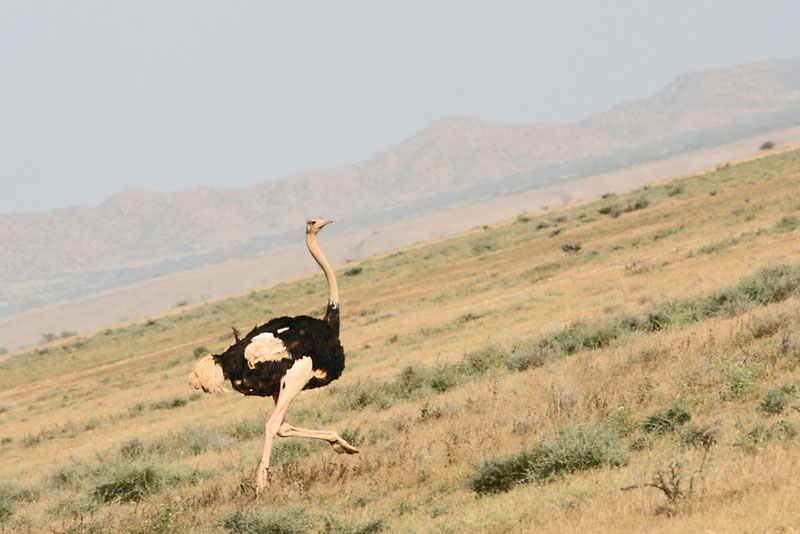
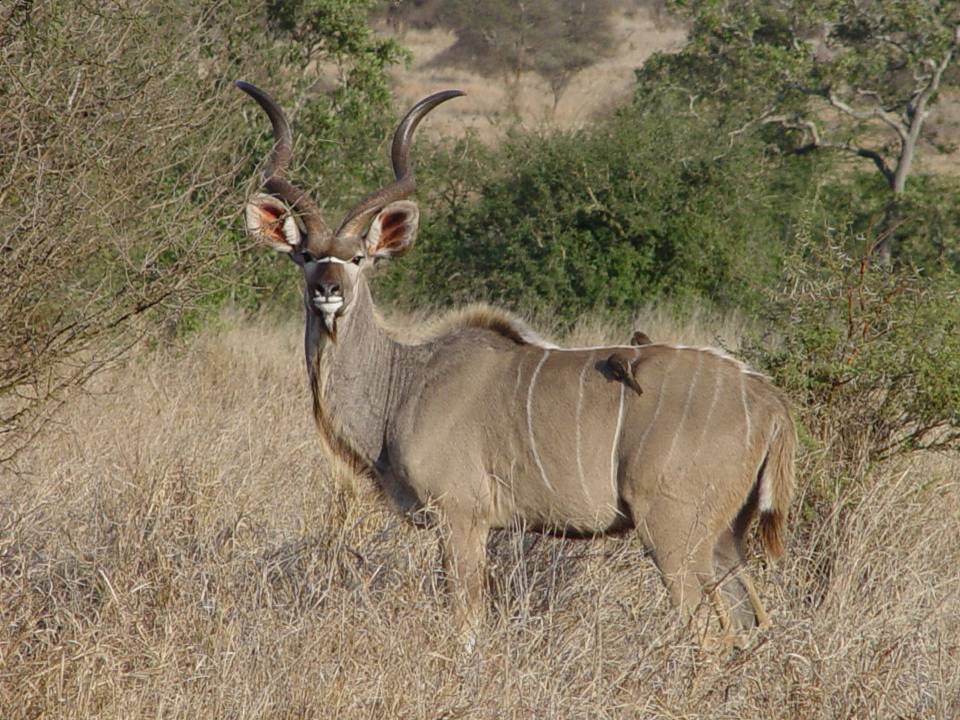
Eritrea has recorded the presence of approximately 600 bird species and is a very important migration route and stopover location for many species. A total of 90 reptiles and 19 amphibian species have been recorded in Eritrea, including two possibly endemic reptiles and one possibly endemic amphibian. Offshore areas are important for turtle foraging and nesting of sea turtles. There is no comprehensive plant inventory for the country, but one site has recorded almost 700 species. Eritrea is recognized as a centre of origin and diversity for a number of crop species, and has major areas of mangroves and seagrasses. The country also has a remarkable diversity in seaweeds, halophytes, and plankton. There is a high diversity of corals and fish, with at least 38 coral genera representing 220 species, some of which are endemic to Eritrea. Eritrea is also home to five of the world’s seven marine turtle species and a large number of cetaceans, as well as a wide range of invertebrates. Finally, Eritrea is home to a number of globally rare mammal species, including the African wild ass (Equus africanus) and the Nubian ibex (Capra nubiana).
Pressures and Threats
One of the largest direct threats to biodiversity in Eritrea is habitat transformation, due to expansion of agriculture and pollution of freshwater and marine ecosystems, as well as transformation for urban and industrial development. Seagrass and seaweeds are impacted by increasing sedimentation. Invasive alien species are major threats. Deforestation and excessive pollarding are impacting forest resources. Illegal hunting of wildlife for the bushmeat trade is an issue, particularly in grassland ecosystems. Overharvesting of corals, fish and other marine species represent serious pressures on these species. Invasive species are a threat to many species and ecosystems, including predatory mammal species which prey on island breeding birds. Sea turtles are threatened by the disturbance of nesting sites, poaching of eggs and illegal hunting of mature animals, as well as bycatch in trawlers.

 Protected Areas
Protected Areas





