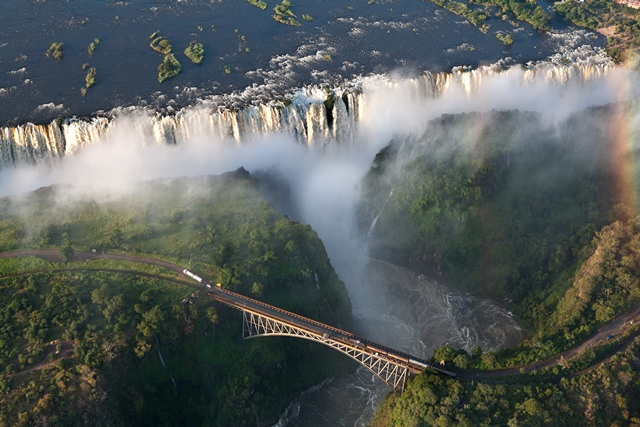
Zambia is a land locked country in southern Africa comprising forests, agro-ecosystems and wetlands as the most important ecosystems to the national economy and rural livelihoods. Biodiversity conservation to date has been undertaken through the management of the existing protected areas system, and promotion of sustainable utilization of natural resources in open areas.
The key changes in the status of National Parks, Forest reserves and the Game Management protected area system since 2009 have been the creation of a new Lusaka National Park, degazetting of some forest reserves and the identification of gaps of representation of plant and animal species within the existing National Parks and Game Management Areas as far as possible by the reclassification conservation plan.to guide conservation action
Transboundary protected and conserved areas
Zambia includes parts of six transboundary conservation areas, namely Kavango-Zambezi TFCA, Liuwa Plain-Mussuma TFCA, Lower Zambezi-Mana Pools TFCA, Malawi-Zambia TFCA, Mosi-oa-Tunya / Victoria Falls Transboundary World Heritage Site, and ZIMOZA TFCA.
Policy context
A comprehensive report on legislation and policy related to protected area management, governance, and equity was undertaken by the BIOPAMA programme. It identified 79 relevant laws and policies in Zambia (Tessema, 2019).
Key species
Zambia is home to over 12,500 species, of which almost 200 have been assessed as threatened according to the IUCN Red List. Almost 4,000 plant species and 563 microorganisms have been recorded. 224 mammal species have been recorded, many of which are economically important through hunting and tourism. Zambia is also home to over 750 bird species, comparatively high for a landlocked country dominated by a single biome. 490 species of fish have been recorded
Pressures and threats
Zambia’s ecosystems face major threats: de-gazettement of forest reserves, mostly for purposes of mining; deforestation and habitat degradation; human encroachment into protected areas; uncontrolled late bush fires; over-exploitation of certain tree species, as well as mammals for the bush-meat and illegal wildlife trade and over-fishing of freshwater ecosystems; pollution from agriculture, mining and other industrial activities; and alien invasive species.

 Protected Areas
Protected Areas





